It is very rare in osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine against cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis.
It’s about the structure of the chest region: it has more discs than the neck and lumbar combined, the discs are smaller and thinner. The mobility of this section is usually lower, with the ribs and sternum taking on part of the load.
In osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, symptoms can be confused with, for example, a heart attack. This is due to the specifics of the disease.
Painful pain during exercise and exertion, such as osteochondrosis of the neck or lumbar spine, does not occur in this case, and complications associated with suspected angina pectoris or myocardial infarction or impaired respiratory function come to the fore.
Causes
The development of osteochondrosis is more facilitated by hypodynamics - a lack of muscle load, which results in a lack of training in the muscular corset, a weakening of its functions, and an increase in the load on the ligaments and intervertebral discs.
The following conditions can also cause osteochondrosis:
- Improper posture and lateral curvature of the spine;
- Bad habits;
- Nervous and physical exertion, stress;
- Back and spine overload when wearing high heels, during pregnancy and on flat legs;
- Back injuries;
- Hypodynamics;
- Inheritance;
- Physically hard work.
The intervertebral discs of the thoracic vertebrae are equally affected by sedentary lifestyle and physical activity, which increases the likelihood of injury.
What is the specificity of the thoracic spine?
Everyone knows that the chest region is functionally inactive, especially relative to the neck. And the load is not that great, for example, compared to the lumbar spine. Because of this, the incidence of disease of the chest region is quite rare, the symptoms appear at an early stage of development.
The low mobility of the thoracic spine is related to its anatomical features - the connection of the vertebrae to the ribs and sternum allows the formation of a sufficiently mobile and at the same time strong structure that is less sensitive to injuries and external influences.
The relatively low workload of this department contributes to the fact that the problems that occur in it (e. g. , vertebral displacement, intervertebral hernia, protrusion of the disc) are quite rare, as confirmed by statistics. However, their appearance cannot be called something extraordinary, for example, poor posture and scoliosis can be some of the provoking factors for the occurrence of spinal diseases.
However, the symptoms of such diseases appear quite late and are quite characteristic of osteochondrosis - usually compression of the nerve roots, in rare cases compression of the spinal cord itself or damage due to a violation of the blood supply, and compression of the veins.
Symptoms of Chest Spinal Osteochondrosis
The symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine can be completely different, similar to the manifestations of other diseases of the internal organs. Often, thoracic osteochondrosis is mistaken for coronary artery disease, cholecystitis, gastric ulcer, and even myocardial infarction and pneumonia. To do this, this disease is called a "chameleon. "
Pain Symptoms:
- Pain is localized under the shoulder blades and can radiate to the intercostal nerves. This leads to neuralgia. The pain increases when a person takes a breath, actively moves.
- Chest pain is most often localized to the left and may resemble ischemic heart disease. In this situation, it is important to find out the cause of the pain in time. A complete examination of the cardiovascular system is required.
Neurological symptoms:
- Numbness or “goosebumps” in the legs, upper chest and abdomen (depending on the disc involved);
- Reflex tension in the chest or upper back;
- In particularly advanced cases, it is possible to disrupt the function of the pelvic organs, and in men it may be less potent.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine may include pain in the upper abdomen, heart, liver, and gallbladder in addition to spinal and back pain, near the localization of osteochondrosis.
When such pain occurs, it is sometimes possible to make a misdiagnosis. The pain under the ribs on the right side of the chest can be confused with inflammation of the gallbladder, and on the left side of the chest - can be confused with a heart attack. Fault is false pain in the appropriate areas of the abdominal cavity due to the manifestation of gastric ulcer or gastritis.
Dorsago
Dorsago is a symptom of osteochondrosis of the chest spine, manifested by acute pain. Usually, this symptom occurs in people who sit in a position or uncomfortable position for a long time, performing monotonous work in a monotonous manner.
There may be pain in the spine of the chest region, the muscles are tense and it is often difficult to breathe. Intercostal neuralgia may occur.
Dorsalgia
The flare-up period lasts 2-3 weeks. In this case, the painful feelings gradually increase. Mild pain appears in the affected spine. As a general rule, pain occurs particularly actively with deep breathing and bending forward, backward, sideways.
The nature of dorsalgia pain can be very different. The pain can be pulling, burning, sore, cutting, can be given under the feet, arms, buttocks, scapula. In terms of localization, the pains are no less varied. They may appear at the bottom, top, center, right, left, between the shoulder blades.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
X-ray-based diagnostic data will assist in developing a treatment plan for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the chest region. Such a study provides a clear picture of the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis because X-ray readings indicating the growth of vertebral bodies and the presence of changes in intervertebral distance (decrease in height) are characteristic symptoms of this disease.
The treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine depends on the stage of the disease and is mainly reduced to conservative therapy. Surgery is extremely rare for spinal hernia.
Medication
Drug therapy is based on the following principles:
- Use of a special drug that allows fluid to be retained on the intervertebral disc.
- Vitamins. Most commonly, complete vitamin complexes or preparations are prescribed with B-group elements
- Anticonvulsants and muscle relaxants that reduce spasm in the muscles surrounding the spine.
- Analgesics. NSAIDs and analgesics based on drug combinations.
- Chondroprotectors. It is essential to catalyze the process of repairing damaged cartilage.
After the elimination of acute events, the muscles of the back and lower limbs are massaged. Hand therapy is indicated in 1-3 degree osteochondrosis in the formation of functional blocks. It contains a variety of options for the soft and rough effects of the back muscles.
The duration of treatment for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine depends on the severity of the disease and the extent of age-related changes, as well as the patient's diligence in meeting the prescribing physician's instructions.
Exercise in chest osteochondrosis
With osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, patients are prescribed therapeutic exercises with the primary goal of increasing the mobility of the rib vertebrae and intervertebral joints. Exercise therapy (with regular and correct exercise) allows you to eliminate even very strong muscle cramps. Moderate physical activity helps relieve spinal stiffness, which occurs with a weak muscle splint.
Daily activities, under the supervision of an experienced instructor, will have a beneficial effect on the whole body in general and the bronchopulmonary system in particular. Patients will have improved lung ventilation and will be able to perform deep breaths and exhalations painlessly.
Massage

Massage not only weakens the severity of the symptoms of the disease, but also helps the person to heal, the efforts have a positive effect on other elements of complex therapy.
The clinical picture of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is prescribed individually based on chronic diseases and contraindications.
Manual therapy
manual therapy is used to eliminate muscle hypertension and cramps and to restore back mobility. Manual therapy promotes the release of blood vessels, improves the nutrition and oxygen supply to the tissues of the intervertebral disc.
Correct position at rest and during sleep
To prevent osteochondrosis and during the treatment period, proper rest and sleep should be organized. It’s best to sleep on an even and hard bed, but to avoid being fanatical if the bed doesn’t meet the requirements, it’s not recommended to sleep on the floor so you can catch a cold. This measure is very necessary for the spine to regain its normal shape quickly.
At first, however, a rather intense painful sensation may appear, which lasts until the vertebrae are in a physiological state. You can place a roller under the affected area to relieve pain and discomfort.
Exercises
The most effective treatment for muscle cramps is physiotherapy. Well-chosen exercises relax, while strengthening and training your back muscles. As a result, the thoracic spine is stabilized, and the choked spinal nerves are released.
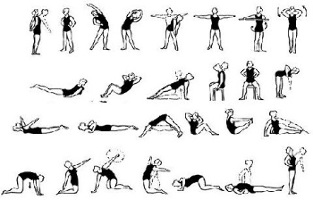
The chest osteochondrosis exercise sequence is performed as follows:
- Starting position - stand up while inhaling, legs straight, arms down. Extend your arms - exhale, then lean back - take a deep breath. Lower your arms, lean forward, round your back, and lower your shoulders and head - exhale. Perform 8-10 repetitions.
- Starting position - sitting on a chair. Slowly put your hands behind your head - inhale, fold back five times, leaning against the back of the chair with the shovel - exhale.
- Starting position - get on all fours and bend your back as much as possible, hold for 3 seconds and keep your head straight for three. Perform 5-7 repetitions.
- Starting position - comfortable to lie on your stomach and rest your hands on the floor. At the same time, lean back with force and try to tear your body off the floor. Perform 5 to 8 repetitions.
- Starting position - lying on your stomach with arms along your body. Bend your chest, trying to raise your head and legs as much as possible. Perform 5 to 8 repetitions.
If you follow all of your doctor's prescriptions, you can slowly but surely make significant improvements.
Prevention
May damage your chest and other parts of your spine:
- long static load (on TV, sitting in front of computer);
- weight lifting;
- slouching habit;
- Hypothermia and frequent colds.
Office workers who sit in the on-call workplace need to change their position more often, get up, and do physical exercises. Even simple stretching is advantageous.



































